X.com Steve Reiner @stevereiner LinkedIn Steve Reiner LinkedIn Posts
Flexible GraphRAG or Flexible RAG, an Apache 2.0 open source python platform, is now flexing to the max using LlamaIndex, in terms of supporting more databases and data sources: supports 8 graph databases, 10 vector databases, 3 search engines, and 13 data sources,. Also supports knowledge graph auto-building, schemas, LlamaIndex LLMs, Docling doc processing (LlamaParse coming soon), GraphRAG mode, RAG only mode, Hybrid search, and AI query / chat. Has React, Vue, and Angular frontends, and a FastAPI backend. React, Vue, Angular, Backend now work on Windows, Mac, Linux (standalone or in docker). Also has a FastMCP MCP server. Has a convenient docker compose that can include any of the databases (Vector, Graph, Search, Alfresco) and Dashboards / Consoles.
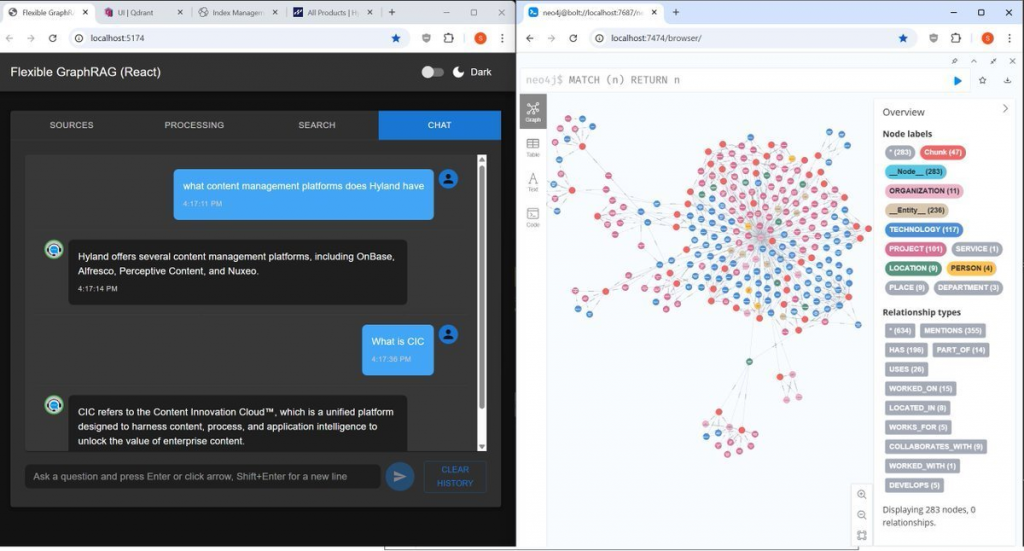
(Flexible GraphRAG AI chat shown with Hyland products web page(s) used with web pages data source to auto-generated a Neo4j graph).
Convenient docker compose: you can choose to include from all supported 10 vector and 8 graph databases, Elasticsearch, OpenSearch, and Hyland Alfresco Community. Include in the docker-compose.yaml by just removing the # comment in front of their includes. Dashboards / Consoles for these databases, as much as possible are also included in the docker compose choices (either in the yaml file for the database or for some a separate yaml file include).
You can run the docker with the databases with the backend and frontends (React, Angular, Vue) running stand alone in separate terminal windows. In addition to running the databases in docker, you can include the backend and frontends in the dock compose by including the app-stack.yaml and proxy.yaml includes. Now have no config duplication for standalone backend+frontends vs full docker mode: previously had to repeat all config in app-stack.yaml now use env_file: include standalone backend .env and overrides with include of docker.env (for configs that need host.docker.internal)
All 8 Graph database working: Neo4j, ArcadeDB, FalkorDB, archived Kuzu (LadybugDB fork todo), NebulaGraph, Memgraph, Amazon Neptune, Amazon Neptune Analytics
All 10 Vector databases working: Qdrant, Elasticsearch vector, OpenSearch vector, Neo4j vector, Milvus, Weaviate, Chroma (both http, embedded), Pinecone, PostgreSQL + pgvector, LanceDB
All 3 Search engines working: Elasticsearch, OpenSearch, LlamaIndex built-in BM25
New Data Sources: using LlamaIndex readers: 1. working ones that don’t use document processing: Web Pages, Wikipedia, Youtube, 2. working using document processing: S3, 3. ones using document processing still to test: Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, Azure Blob, GCS, Box, SharePoint.
Support for Docling document processing is currently available. Being able configure to use LlamaParse coming soon.
Original data sources with document processing that don’t use LlamaIndex readers: filesystem, Alfresco, CMIS. Hyland Alfresco Community can be included in the docker compose by taking the “#” comment off the beginning of its include.
LLMs: LlamaIndex LLMs (LlamaIndex has support for very many), Flexible GraphRAG currently has config for 1. tested, working: OpenAI, Ollama, 2. untested: Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, Azure OpenAI.
Previous Flexible GraphRAG posts:
See Flexible GraphRAG Initial Version Blog Post
See New Tabbed UI for Flexible GraphRAG (and Flexible RAG)
See Flexible GraphRAG: Performance improvements, FalkorDB graph database support added
See Flexible GraphRAG: Supports ArcadeDB Graph Database with new LlamaIndex Integration
See Flexible GraphRAG: Amazon Neptune, Neptune Analytics, and Graph Explorer support added